January 25th, 2017
North Dakota is uniquely situated to lead the way on carbon capture, utilization and storage solutions. It has an abundant supply of coal and geology suitable for CO2 storage as well as oil fields available for enhanced oil recovery.
November 30th, 2016
There is a growing consensus among industry, the environmental community and governments that future CO2 emission reduction goals cannot be met by renewable energy sources alone and that carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) technologies for all fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) will have to be deployed to achieve climate objectives in the U.S. and globally. A commitment to deploying CCUS technologies begins with policies and incentives to level the playing field for CCUS, and includes advancing efforts to deploy CO2 utilization technologies and products.
October 27th, 2016
This panel will discuss the Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Act (S. 3179), introduced by Sens. Heidi Heitkamp (D-ND), Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) and Shelley Moore Capito (R-WV). This act would remove the cap currently on the Section 45Q federal tax credit. In addition, it would increase the value for each ton of CO2 captured and stored from power plants and industrial facilities. Lawmakers from both parties have endorsed this major legislation as it promotes domestic energy security and reduces carbon emissions.
October 7th, 2016
The Government of Tanzania has ambitious plans for increasing access to electricity, improving power reliability, and expanding the use of domestic resources including natural gas and renewable energy. Recent natural gas discoveries in Tanzania and initial investment in transmission infrastructure have made natural gas one of the main anchors of electricity generation.
September 27th, 2016
The IEA Greenhouse Gas R&D Programme is an international collaborative research activity forming part of the IEA’s Energy Technology Network. Its role is to assess the role that technology can play in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel use. The programme is a technical body and interacts with the IEA to ensure its technical messages are translated into policy messages for the IEA Ministers amongst others.
July 26th, 2016
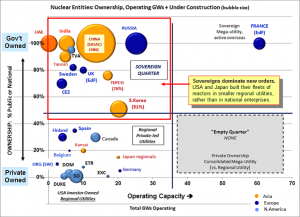
Expanding populations in Asia, high levels of economic growth, and increasing urbanization are combining to create demand for large amounts of reliable and affordable base-load electricity. Governments in Asia and some in the Middle East have recognized this need and have made nuclear power a major part of the energy mix they are developing to meet this demand. China alone is expected to have eight mega-cities (population over ten million) and more than 200 cities with over one million residents by 2030.
July 14th, 2016
The Alberta Energy Regulator operates within the province of Alberta, Canada, and is the single provincial regulator for oil, natural gas, oil sands, and coal development within Alberta.
The AER ensures the safe, efficient, orderly, and environmentally responsible development of hydrocarbon resources over their entire life cycle. This includes allocating and conserving water resources, managing public lands, and protecting the environment while providing economic benefits for all Albertans.
July 14th, 2016
The first large-scale CCS demonstration project, Sleipner, started up in 1996. Over the next two decades, more than a dozen other CCS demonstration projects came on-line. However, there were many more projects that were announced that never came to fruition. By studying both the successful and unsuccessful projects, one can discern patterns and learn valuable lessons that can be applied to future efforts. This presentation summarizes a study that analyzes the financing of large-scale CCS demonstration projects and reports the lessons learned.
June 22nd, 2016
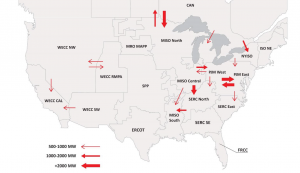
NERC recently published a reliability assessment of the final Clean Power Plan rule – Potential Reliability Implications of EPA’s Clean Power Plan – Phase II. The report finds that combined wind and solar capacity will rise by 10-20 GW over the next 15 years, while coal capacity will decline by up to 27 GW as a result of the CPP. The accelerated transition in the mix of generation resources means a greater emphasis on how renewables and other resources provide essential reliability services – voltage control, load ramping and frequency response.
July 21st, 2016
The presentation will review some of the factors impacting today’s utility business models and the resulting new demands being placed on central generation plants. As renewable energy deployment increases and movement towards lower carbon footprints continues, central station operating profiles are fundamentally changing. New technologies must be developed to maintain grid reliability and enable this transition.
Pages